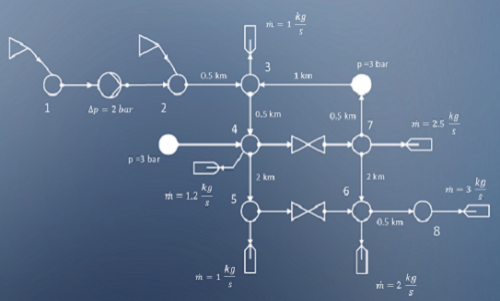
To get started with pandapipes, just
-
Install pandapipes through pip:
pip install pandapipes -
Create a simple network
import pandapipes as pp net = pp.create_empty_network(fluid="lgas") j1 = pp.create_junction(net, pn_bar=1.05, tfluid_k=293.15, name="Junction 1") j2 = pp.create_junction(net, pn_bar=1.05, tfluid_k=293.15, name="Junction 2") j3 = pp.create_junction(net, pn_bar=1.05, tfluid_k=293.15, name="Junction 3") ext_grid = pp.create_ext_grid(net, junction=j1, p_bar=1.1, t_k=293.15, name="Grid Connection") sink = pp.create_sink(net, junction=j3, mdot_kg_per_s=0.045, name="Sink") pipe = pp.create_pipe_from_parameters(net, from_junction=j1, to_junction=j2, length_km=0.1, diameter_m=0.05, name="Pipe 1") valve = pp.create_valve(net, from_junction=j2, to_junction=j3, diameter_m=0.05, opened=True, name="Valve 1") -
Run a pipe flow:
pp.pipeflow(net) -
And check the results:
print(net.res_junction) print(net.res_pipe)
But of course pandapipes can do much more than that - find out what on this page!
Fluid System Analysis
Supports stationary and quasi-stationary analysis of gas and district heating networks.
Free and Open
Published under a BSD License and therefore free to use, modify and share however you want.